Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yuan, X.*; Hu, Q.*; Lin, X.*; Zhao, C.*; Wang, Q.*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Hamamoto, Shoichiro*; Siitari-Kauppi, M.*; Li, X.*
Journal of Hydrology, 618, p.129172_1 - 129172_15, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Civil)Idomura, Yasuhiro
Physics of Plasmas, 26(12), p.120703_1 - 120703_5, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)This Letter presents the impacts of the hydrogen isotope mass and the normalized gyroradius 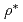 on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like
on L-mode like hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) plasmas dominated by ion temperature gradient driven (ITG) turbulence using global full-f gyrokinetic simulations. In ion heated numerical experiments with adiabatic electrons, the energy confinement time shows almost no isotope mass dependency, and is determined by Bohm like 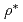 scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of
scaling. Electron heated numerical experiments with kinetic electrons show clear isotope mass dependency caused by the isotope effect on the collisional energy transfer from electrons to ions, and the H and D plasmas show similar ion and electron temperature profiles at an H to D heating power ratio of 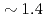 . The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same
. The normalized collisionless ion gyrokinetic equations for H and D plasmas become identical at the same 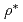 , and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the
, and collisions weakly affect ITG turbulence. Therefore, the isotope mass dependency is mainly contributed by the 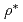 scaling and the heating sources.
scaling and the heating sources.
Tobita, Toru; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Otsu, Takuyo; Udagawa, Makoto; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 137(5), p.051405_1 - 051405_8, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:54.45(Engineering, Mechanical)We conducted a series of fracture toughness tests based on the Master curve method for several specimen size and shapes, such as 0.16T-CT, pre-cracked Charpy type, 0.4T-CT and 1T-CT specimens, in commercially manufactured 5 kinds of A533B class1 steels with different impurity contents and fracture toughness levels. The reference temperature ( ) values determined from the 0.16T-CT specimens were overall in good agreement with those determined from the 1T-CT specimens. The scatter of the 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values obtained from the 0.16T-CT specimens was equivalent to that obtained from the other larger specimens. The higher loading rate gave rise to a slightly higher
) values determined from the 0.16T-CT specimens were overall in good agreement with those determined from the 1T-CT specimens. The scatter of the 1T-equivalent fracture toughness values obtained from the 0.16T-CT specimens was equivalent to that obtained from the other larger specimens. The higher loading rate gave rise to a slightly higher  , and this dependency was almost the same for the larger specimens. We suggested an optimum test temperature on the basis of the Charpy transition temperature for determining
, and this dependency was almost the same for the larger specimens. We suggested an optimum test temperature on the basis of the Charpy transition temperature for determining  using the 0.16T-CT specimens.
using the 0.16T-CT specimens.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Takahashi, Shoji*
Scientometrics, 78(3), p.505 - 524, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:24.99(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)A socio-economic evaluation of Material Science (MS) of JAERI was made. The goal was to reveal the emphasized basic research fields (EBRF) of MS and to observe its socio-economic networking. High ranked keywords for the former and the number of co-authored papers for the latter were used along with many MS related papers. The obtained results are: (1) The EBRF of MS of JAERI were typically represented by the keywords of ion irradiation, actinides, etc., i.e., those having a strong relation to the nuclear field. Regarding actinides, the socio-economic networking between JAERI and PS occurred at the growth rate of 3-4% per 25 years, but 8% during the past 5 years. This implies that the research cooperation between the two was markedly enhanced. (2) The EBRF of MS between JAERI and 5 selected research bodies (SRB) represented by Tokyo University was directly compared and revealed that only 7 keywords as typically represented by neutron and accelerators. After overlapping, JAERI and SRB seem to be raising the national standard level.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki; Takahashi, Shoji; Narita, Osamu; Yonezawa, Minoru
IAEA-CN-123/03/P/18 (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2004/10
To understand a socio-economic effect of basic research in JAERI, the stimulation and promotion of social interrelations through a formation of networking was studied quantitatively. (1)Worldwide trend of MS was studied by INIS by means of top {100} keywords as input. Research activity of MS in JAERI represented by top {100} keywords is not much different from that of other nuclear advanced countries participated to INIS. (2)Emphasized basic research fields (EBRF) of MS in JAERI can be clarified by selected keywords of "ion irradiation" and "actinides", those have a strong relation to nuclear. For actinides, the growth rate of networking between JAERI and PS was of order of 3-4% per 25 years and 8% per recent 5 years. The rate of networking formation is markedly increased recently. (3)Between JAERI and the other 5 selected research bodies, only 7 out of over 110 keywords such as "neutron" and "accelerators" were overlapped. In the overlapped region the two compensated and uplifted the national standard level each other.
Onizawa, Kunio; Suzuki, Masahide
JSME International Journal, Series A, 47(3), p.479 - 485, 2004/07
In the structural integrity assessment of reactor pressure vessel, fracture toughness values are estimated by assuming that the radiation effect on fracture toughness is equivalent to that on Charpy properties. Therefore, it is necessary to establish the correlation between both properties especially on irradiation embrittlement. In this paper, we present the fracture toughness data obtained by applying the master curve approach that was adopted recently in the ASTM test method. Materials used in this study are five ASTM A533B class 1 steels and one weld metal. Neutron irradiation for Charpy-size specimens as well as standard Charpy-v specimens was carried out at the Japan Materials Testing Reactor. The shifts of the reference temperature on fracture toughness due to neutron irradiation are evaluated. Correlation between the fracture toughness reference temperature and Charpy transition temperature is established. Based on the correlation, the optimum test temperature for fracture toughness testing and the method to determine a lower bound fracture toughness curve are discussed.
The Ad Hoc Committee for Evaluation of R&D Achievements
JAERI-Review 2003-036, 75 Pages, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
 fuels
fuelsUne, Katsumi*; Nogita, Kazuhiro*; Suzaka, Yojiro*; Hayashi, Kimio; Ito, Kunio*; Eto, Yoshinori*
International Topical Meeting on Light Water Reactor Fuel Performance, 2, p.775 - 785, 2000/00
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Hiroshi; Naito, Yoshitaka; *
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 31(9), p.986 - 995, 1994/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:28.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Jitsukawa, Shiro; Kizaki, Minoru; ; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Hishinuma, Akimichi
Small Specimen Test Techniques; ASTM STP 1204, p.289 - 307, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:98.51(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
; Sato, Osamu; ; *
Nucl. Eng. Des., 136, p.211 - 217, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 fuel grain size on reactivity; Continuous energy Monte Carlo calculations
fuel grain size on reactivity; Continuous energy Monte Carlo calculationsSakurai, Y.*; Okuno, Hiroshi; Naito, Yoshitaka
JAERI-M 91-137, 35 Pages, 1991/09
no abstracts in English
 -fuel grain size on reactivity; Study by ultra-fine energy group calculations using the computer codes based on the collision probability method
-fuel grain size on reactivity; Study by ultra-fine energy group calculations using the computer codes based on the collision probability methodOkuno, Hiroshi; *
JAERI-M 91-107, 49 Pages, 1991/08
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Hiroshi; Komuro, Yuichi; Naito, Yoshitaka
Proc. of the 91 Int. Conf. on Nuclear Criticality Safety,Vol. 1, p.III-38 - III-43, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
Okuno, Hiroshi; Komuro, Yuichi; Naito, Yoshitaka
Proc. of the CSNI Specialist Meeting on Safety and Risk Assessment in Fuel Cycle Facilities, p.103 - 109, 1991/00
no abstracts in English
; Sato, Osamu; ; *
Proc. for the Seminar on 10th Int. Conf. SMiRT, p.VI.6.1 - VI.6.8, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
Sudo, Yukio; Nakajima, Hajime
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 19(1), p.34 - 45, 1982/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:40.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English